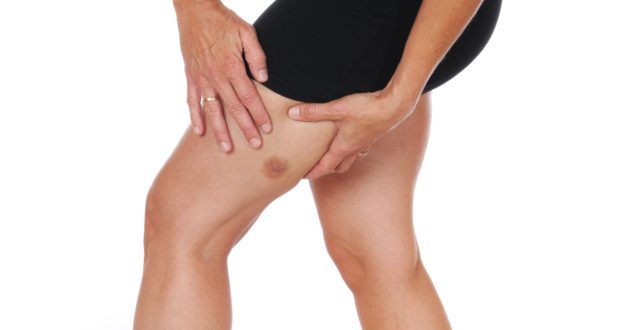
Bruises are kind of like mosquito bites or paper cuts, in that virtually everyone gets them at some point or another. Some people rarely deal with bruises, while for others they are a recurring problem. Though there is no surefire way to avoid this kind of injury, taking some preventative measures can help prevent bruises from forming on your skin.
Definition of a Bruise
Also referred to as contusions, bruises occur when the body’s soft tissues are injured, forcing small blood vessels (called capillaries) inside them to break. Red blood cells then leak out of these ruptured vessels, causing the skin discoloration commonly associated with bruising. After sustaining a bruise, the affected area can take on a blue, purple, red or black tinge.
As the body begins to heal its damaged tissues, the color of the bruise itself begins to change. For example, a bruise may initially have a red or purple appearance. In addition, there’s a good chance that it will also be noticeably tender and sensitive to touch. The bruise could then turn a blue or black few days afterwards.
Five to ten days after the bruise first forms, the bruised area might have a greenish or yellow look. At the ten to fourteen day mark, the bruise’s color will probably be light brown; at this point, the contusion will likely fade away completely in a matter of days. Generally speaking, bruises stick around for about two weeks before vanishing.
Reasons for “Easy Bruising”
Certain factors can increase a person’s risk of bruising:
Blood Clotting Medications – Some people take certain medicines in order to prevent the formation of blood clots, which can cause serious health problems like strokes and heart attacks. Unfortunately, such drugs can increase the bleeding from ruptured capillaries, causing bruising to occur on a more frequent basis.
Dietary Supplements – Certain dietary supplements, such as fish oil, may cause blood to become thinner. In turn, this increases the body’s bruising risk.
Age – As with other parts of the body, age can take its toll on our blood vessels, rendering them more susceptible to breaking. Making matters worse is that vessels have significantly less insulation in the body’s older years, as the skin loses much of its thickness.
Medical Conditions – Conditions like hemophilia, leukemia, end-stage kidney disease can all make bruises more likely.
Treating and Preventing Bruises
Many bruises can be treated with the RICE method, an acronym standing for Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation.
Rest – Rest allows the bruise to heal and helps protect the injured area from further damage.
Ice – Ice packs can be used to prevent (or at least reduce) the swelling caused by bruises. Hold the ice pack against the bruise at least three times per day, for a period of ten to twenty minutes.
Compression – Applying an elastic bandage to a bruise can alleviate bruise-related swelling. However, be careful not to wrap the bandage too tightly around the contusion, as this might actually increase the level of swelling. A bandage that has been applied excessively tight manner might also lead to numbness, tingling, pain or swelling below the bandaged area.
Elevation – If possible, prop up the bruised area so that it is at or above heart level. When either lying down or sitting, you can elevate the injured body part with pillows.
The US National Library of Medicine advises calling your health care provider for contusions that cause feelings of extreme pressure. This advice also applies to bruises that exhibit signs of skin infection or appear for no apparent reason.
Following some common-sense steps can help prevent bruising of the skin. Those who play certain sports, for instance, can wear padding over areas susceptible to bruises. Thigh pads, elbow pads and hip guards all are used to shield both football and hockey players from injury. Likewise, people who enjoy soccer or basketball might consider putting on knee pads and shin guards.
Of course, bruises can also occur inside your home. Given this fact, it’s a good idea to exercise a proper amount of caution when climbing ladders or other objects. Wearing a seat belt can protect the body from a wide range of driving-related injuries, including bruises. Finally, parents should encourage young children to stick to safe playtime activities.
 Natural Knowledge 24/7 Educate yourself with nutrition, health and fitness knowledge.
Natural Knowledge 24/7 Educate yourself with nutrition, health and fitness knowledge.